GraphQL 简介
GraphQL 是什么?其解决什么问题?什么场景下使用GraphQL?原理是什么?
GraphQL 是什么?
GraphQL是 Graph Query Language的缩写,和你想的一样,其最广泛的用途就是查询数据。 GraphQL由Facebook于2015年开源。
定义:
GraphQL is a query language for your API, and a server-side runtime for executing queries using a type system you define for your data.
GraphQL 解决什么问题?
其主要尝试解决现有的数据查询方案REST API 所暴露的问题,包括:
- 过度获取(Over-fetching)
例如前端只需要一个Student的姓名,下面是使用REST API 与 GraphQL查询的对比
REST:
{
"id":"1100000"
"name":"Shusheng007",
"age":18,
"grade":"grade 2",
"family_address":"good place"
"school":{
"name":"NiuBi74110",
"location":"xxxxxxxx"
}
}
Graph:
query{
student(id:"1"){
name
}
}
可见,使用REST API 查询到了很多用不上的信息,而GraphQL只查询了说需要的数据,这就是所谓的过度获取
- 欠缺获取(Under-fetching)
假如前端需要查询一个Student的详细信息,下面是通过REST API 与GraphQL查询的情况
REST:
使用REST需要查询API1 与API2然后将结果组合起来才能获取到需要的信息,所以单个API无法获取到足够的信息叫做欠缺获取
get from API1:
{
"id":"1100000"
"name":"Shusheng007",
"age":18,
"grade":"grade 2",
"family_address":"good place"
}
get from API2:
{
"name":"NiuBi74110",
"location":"xxxxxxxx"
}
GraphQL:
query {
student(id:"1"){
id,
name,
age,
grade,
family_address,
school {
name,
location
}
}
}
可见,GraphQL一次查询就获取到了说需要的信息。
- 版本迭代
对一个获取Student的REST API,随着开发的进行将不断地迭代,有可能产生很多个版本
API 第1版 v1/xxx
API 第2版 v2/xxx
什么场景下使用GraphQL
清楚一项技术适合什么场景非常非常重要,一定要认真对待。下面列举了一下GraphQL的一些适合的应用场景
多客户端的应用
例如应该应用服务多种客户端:Android、IOS、Web、各种小程序
前端展示高度灵活的应用
例如,内容管理系统(CMS)、仪表盘(Dashboard) 或报表页面
性能或网络敏感的场景,尤其是移动端
例如要支持在某个网络环境很差的地区运行的移动端APP
GraphQL 原理是什么?
GraphQL 本质上是一种查询语言和执行引擎。
- 查询语言:客户端以声明式语法(类似 JSON)描述自己需要的数据。
- 执行引擎:服务端根据查询请求执行对应的 resolver(解析器),并返回结果。
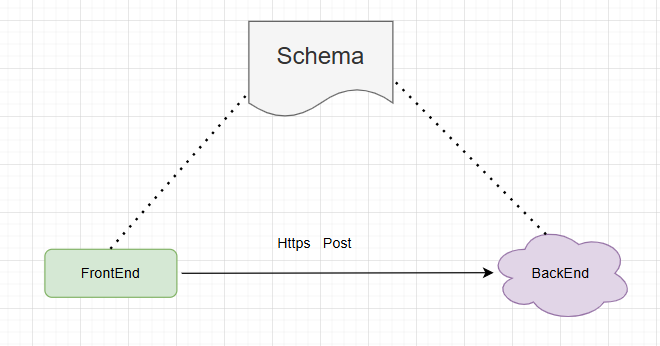
工作流程:
- 客户端向 GraphQL 服务器发送一个查询字符串;
- 服务器解析这个查询;
- 服务器根据 Schema 中的定义调用相应的 resolver 方法;
- 返回结果,结构与查询保持一致。
核心概念
当学习一门新技术时,首先要弄清楚的就是你核心概念,当清楚了其核心概念后,就算是入门。
- Schema:
GraphQL核心中的核心,Schema设计的好坏直接影响GraphQL的表现,非常重要!其是GraphQL的数据模型描述,前后端交互的统一语言。前端通过它明确自己能查啥,怎么查;后端通过它明确自己应该提供啥,怎么提供。
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String
}
type Query {
user(id: ID!): User
users: [User]
}
type Mutation {
createUser(name: String!, email: String): User
}
一般使用SDL (Schema Definition Language): 来写 Schema,上面是一个示例
文中定义了3个类型,User 、Query 和 Mutation ,其中User是自定义类型,而后两个是GraphQL的built-in类型。 Query定义支持哪些查询,Mutation 定义支持哪些修改
- Types:
类型其实就是用来表明数据是什么,能干什么的一个标志。例如,Int 类型表明它是一个整形数字,这种类型的数据只能做它允许的行为,例如算术运算。
GraphQL提供了很多数据类型:
Scalar(标量):
Int、Float、String、Boolean、ID。最小单元无法再包含其他类型。
Object(对象):
Query,Mutation,Subscription,自定义类型,例如上文的User
其他类型: Enum、Interface、Union、List
- Query:
相当于 REST 的 GET,用来查询数据。
- Mutation:
相当于 REST 的 POST/PUT/DELETE,用来修改数据。
- Subscription:
基于 WebSocket 的实时订阅机制(事件驱动)。
- Resolver:
Schema中每个字段对应的实现逻辑,提供数据。(通常是调用数据库或外部 API)。
实践
由于GraphQL最广泛的使用是查询数据,所以我们这里只演示Query,Mutation 与Subscription留作以后探索
由于我惯用Java,所以这里就结合SpringBoot来展示如何使用GraphQL.
引入依赖
SpringBoot 集成了GraphQL Java,提供了开箱即用的starter,所以引入如下依赖即可。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-graphql</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
因为GraphQL需要特殊的客户端才能访问,我们可以通过application.yml 配置来使用GraphQL的客户端Graphiql。当然我们也可以使用其他客户端,例如Postman, Insomnia等
spring:
graphql:
graphiql:
enabled: true
创建Shcema
在 resources/graphql路径下创建后缀为 .graphqls的文件,例如 post.graphqls
type Post {
id: ID!
title: String!
content: String!
category: String
author: Author!
}
"""
The person who write the post
"""
type Author {
id: ID! #the id of author
name: String!
thumbnail: String
posts: [Post]!
}
# The Root Query for the application
type Query {
fetchAuthor(authorId: String): Author!
fetchRecentPosts(count: Int):[Post]!
}
值得一提的是,这个路径是默认路径,可以通过 application.yml文件更改,但是大部分情况下使用默认的即可。
我简单介绍一个这个schema。Schema中创建了两个自定义类型Post和Author,一个Query,提供了两个查询操作。
我们以下面的片段为例介绍一下graphql的语法
- 文档
"""
The person who write the post
"""
是graphql的文档,这个文档前端通过graphql的客户端是可以看到的
- 自定义类型
type Author {
...
}
定义了一个自定义的类型Author
- 标量字段
id: ID!
ID 是graphql内置的一个标量类型,其中 !表示非空,即这个值不能为null,后端必须给前端返回value,不然会报错
- 注释
#the id of author
以 #开头的是注释,这个客户端看不见,只给程序看
- List
posts: [Post]!
上面的代码表示,posts是一个item是Post类型的list,且这个list不能是null(由 !指定),你可以是[],但不能是null
实现解释器(resolver)
后端大部分工作会集中在这个部分,其实就是给schema中的field提供数据。Springboot提供了大量的注解来完成这部分
按需查询
我们来展示一下按需查询,SpringBoot为我们提供了各种注解来简化我们的工作。下面是两个Resolver的实现
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Controller
public class PostController {
private final PostDao postDao;
@QueryMapping
public Author fetchAuthor(@Argument("authorId") String authorId) {
return postDao.getAuthorWithoutPosts(authorId);
}
@SchemaMapping(typeName = "Author", field = "posts")
public List<Post> fetchPostsBaseAuthor(Author author){
return postDao.getAuthorPosts(author.getId());
}
}
我们解释一下上面的代码片段。fetchAuthor用来查询某个Author的数据,但是考虑到性能我们将Author的Post列表使用另一个Resolver fetchPostsBaseAuthor来提供。这样做有什么好处呢?
由于前端在查询某个 Author的信息时,有可能不需要其 Post列表,那么我们就可以在 fetchAuthor中不提供此 Author的博客列表。当前端查询需要 Post列表时,Springboot就会先调用 fetchAuthor 后自动调用 fetchPostsBaseAuthor来补齐数据。
输入:
query GetAuthor($authorId: String!) {
fetchAuthor(authorId: $authorId) {
id
name
thumbnail
}
}
输出:
{
"data": {
"fetchAuthor": {
"id": "a-001",
"name": "Dog2Wang",
"thumbnail": null
}
}
}
后端日志:
: fetch authors without post by authorId:a-001
可见只执行了 fetchAuthor 这个Resolver。
输入:
query GetAuthor($authorId: String!) {
fetchAuthor(authorId: $authorId) {
id
name
thumbnail
posts {
id
title
category
content
}
}
}
输出:
{
"data": {
"fetchAuthor": {
"id": "a-001",
"name": "Dog2Wang",
"thumbnail": null,
"posts": [
{
"id": "p-001",
"title": "why we should use graphql",
"category": "API",
"content": "ignore 500 chars"
}
]
}
}
}
后端日志:
: fetch authors without post by authorId:a-001
: fetch posts of specific author by authorId:a-001
可见先后调用了 fetchAuthor 和 fetchPostsBaseAuthor 这两个Resolver。
核心注解
下面让我们看看上面那些神奇的操作是怎么发生的。Springboot 秉承着自己一贯的作风,将复杂隐藏,暴露傻瓜式的使用方式。对应GraphQL也不例外,这不就提供了很多相关注解
@SchemaMapping
使用其标记的方法,作为某一个 Filed的Resolver。例如
@SchemaMapping(typeName = "Author", field = "posts")
其中typeName指定在schema中定义的某个类型,field指定此类型的一个属性
@QueryMapping
其是一个特殊的 @SchemaMapping,专门针对schema中的Query类型。
N+1问题
result:
fetch recent 2 posts
fetch authors without post by authorId:a-001
fetch authors without post by authorId:a-002
高级话题
N+1问题与解决方案
问题:
当请求一个数据列表,列表里的每个元素又有一个字段需要查数据库(或外部服务)时,就可能为每个元素执行一次额外查询,导致性能极差。
假设一个列表有N条记录,每条记录需要查一次,加上查询列表的那1次查询,总共N+1次查询。
解决方案:
- 将N次查询合并为一次查询
- 将N次查询的结果缓存
问题展示:
如果按照我们前面讲过的方法来查询就会出现N+1问题
@QueryMapping("fetchRecentPosts")
public List<Post> fetchPosts(@Argument("count") int numbers){
return postDao.getRecentPosts(numbers);
}
@SchemaMapping(typeName = "Post", field = "author")
public Author fetchAuthorField(Post post) {
return postDao.getAuthorWithoutPosts(post.getAuthorId());
}
输入:
query GetPosts($count: Int!) {
fetchRecentPosts(count: $count) {
id
title
content
category,
author{
id
name
thumbnail
}
}
}
variable
{
"count": 2
}
上面的查询表示查询最近两条博客记录
后端日志:
fetch recent 2 posts
fetch authors without post by authorId:a-001
fetch authors without post by authorId:a-002
可见总共查询了3次,N=2, N+1 = 3.
如何改进:
SpringBoot为此提供了一个注解 @BatchMapping, 将上面的代码改成如下,然后请求使用同样的查询参数查询一下
@QueryMapping("fetchRecentPosts")
public List<Post> fetchPosts(@Argument("count") int numbers){
return postDao.getRecentPosts(numbers);
}
@BatchMapping(typeName = "Post", field = "author")
public Map<Post,Author> batchFetchAuthor(List<Post> posts){
return postDao.getPostAuthorMap(posts);
}
后端日志:
: fetch recent 2 posts
: fetch post-author map: [Post(id=p-001, title=why we should use graphql, content=ignore 500 chars, category=API, authorId=a-001), Post(id=p-002, title=why we should not use graphql, content=ignore 1000 chars, category=API, authorId=a-002)]
可见只有两次查询,N原来是2,现在被合并为1了。当然这是使用了Springboot提供的简单解决方案,数据组合完全托管给了springboot,对于复杂问题你也可以自己管理这个过程。
Federation
GraphQL Federation最先由Applo在2019年提出,后逐渐成为事实标准。Federation 就和微服务架构中的Gateway一样,对于一个复杂的Graphql查询,依据domain会由不同的微服务完成一部分,然后在Federation上进行组合后返回给客户端。
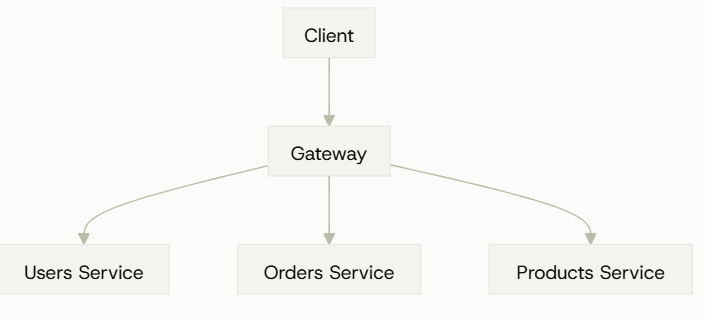
Applo :
总结
本文只是非常简陋的介绍了一下GraphQL的入门知识,如果需要更进一步,可以参考以下资源
源码
你可以从Github找到本文demo的源码:graphql-exploration
